Innovative and Traditional Approaches to Managing Psoriatic Arthritis
Explore the latest and traditional treatments for psoriatic arthritis, including medical options like biologics and DMARDs, as well as effective home remedies like turmeric and Epsom salt baths. Early diagnosis and appropriate therapy are vital to preventing joint damage and improving patient quality of life.
Sponsored
Innovative and Traditional Strategies in Psoriatic Arthritis Care
Understanding the Latest and Conventional Options for Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment
Psoriatic arthritis is a persistent autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of the joints. It often develops after psoriasis, a skin condition with scaly patches, though not everyone with psoriasis develops arthritis. If untreated, it can cause irreversible joint damage over time. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to prevent joint deterioration and improve quality of life. Recognizing symptoms early is key to effective management.
Psoriatic arthritis can affect any joint, including the spine, where it’s called spondylitis, leading to stiffness and mobility issues. It can also cause tender spots in tendons, resulting in heel or back pain.
While many fear permanent joint damage, early intervention can prevent this. When diagnosed promptly, psoriatic arthritis can be managed effectively with various treatments, reducing the risk of long-term harm. Keep reading to explore current and emerging treatment options.
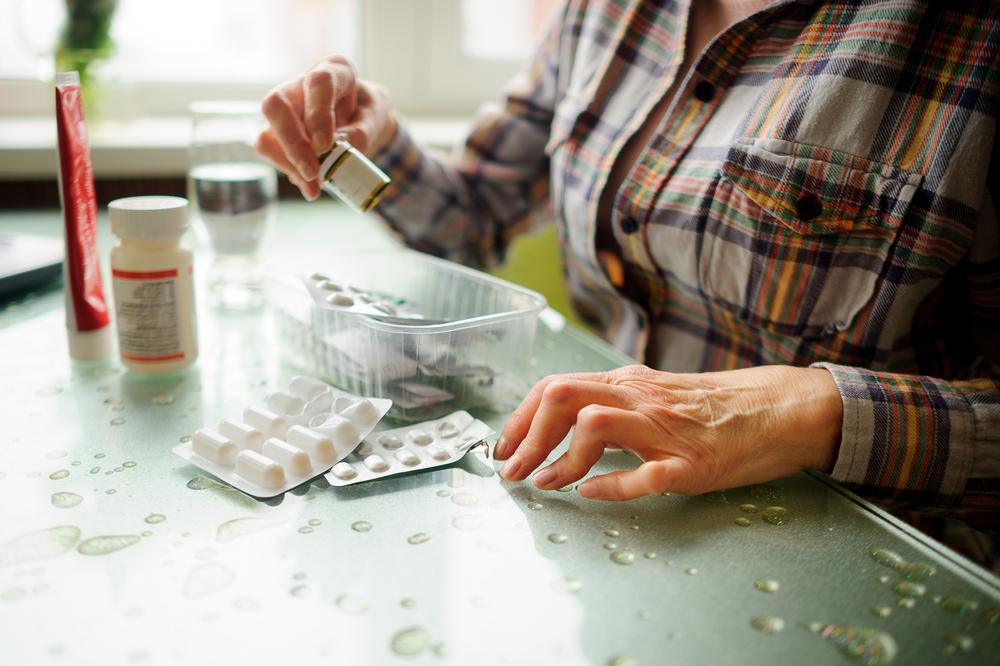
Current therapies for psoriatic arthritis include a variety of medications, both over-the-counter and prescription. These treatments aim to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent joint damage. Available options include NSAIDs, corticosteroids, topical agents, DMARDs, biologics, and phototherapy.
NSAIDs: These drugs alleviate pain and swelling through oral or skin applications.
Corticosteroids: These synthetic hormones help reduce inflammation but may cause side effects such as weight gain or osteoporosis if used long-term.
Topical treatments: Gels and creams applied directly to affected skin target skin symptoms of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
DMARDs: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs suppress inflammation chemicals, helping to prevent joint damage and easing symptoms.
Biologics: Advanced drugs that interfere with cellular inflammation processes; administered via injections or infusions.
Light therapy: Exposing skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision can reduce psoriasis and joint inflammation.
Research continues to yield new options for psoriatic arthritis. Recent FDA approvals include drugs like ixekizumab and tofacitinib, which can be combined with traditional DMARDs for enhanced effect. However, these drugs suppress the immune system, increasing infection risk, so patients are tested for tuberculosis before treatment.
Complementary home remedies can support medical treatments. Herbal options like turmeric, known for anti-inflammatory properties, and Epsom salt baths, rich in magnesium, can alleviate symptoms. Always consult your healthcare provider before combining remedies to ensure safety and effectiveness.