Understanding Joint Degeneration and Bone Weakness: Symptoms, Differences, and Management
This article explains the differences between osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to manage these common age-related conditions effectively. Understanding these conditions can help individuals seek timely medical care to maintain mobility and bone health.
Sponsored
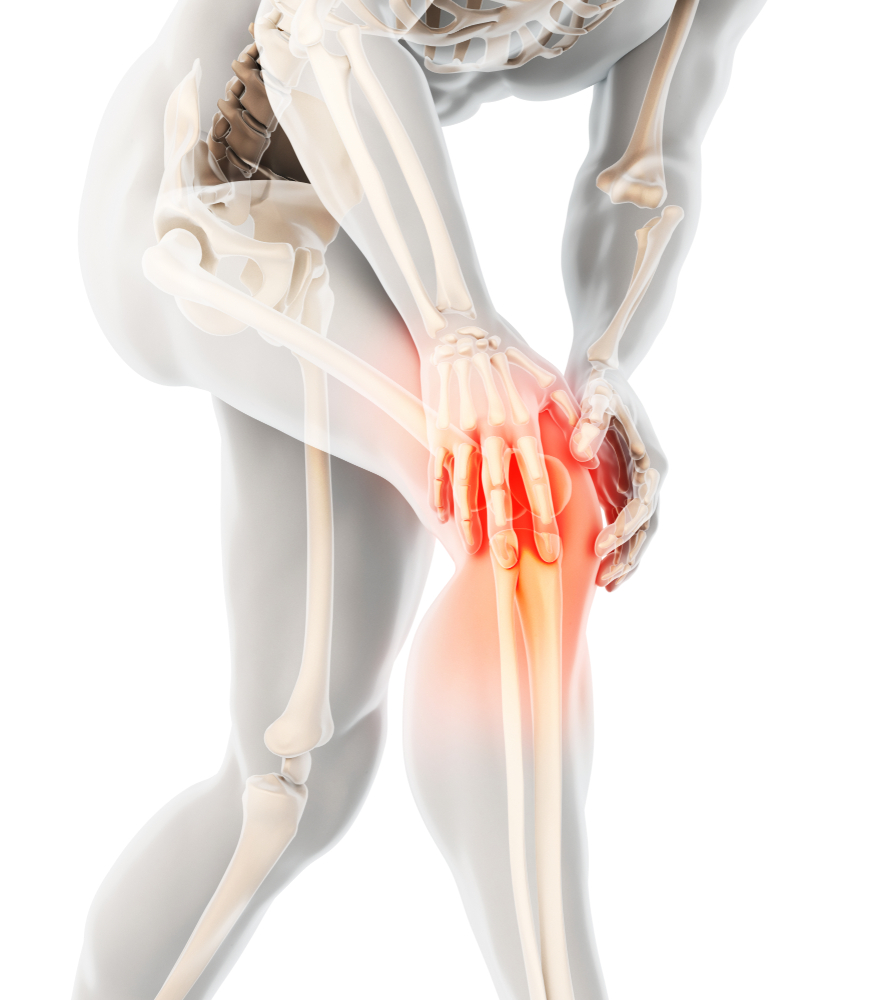
Joint degeneration, known as osteoarthritis, is a common condition that impacts many individuals, especially with age. It leads to difficulty in movement, affecting the ability to walk and perform daily tasks. This condition primarily targets the joints in limbs, causing pain and stiffness. Recognizing osteoarthritis is crucial for effective treatment, which may include medication, physiotherapy, or surgery.
Why does this condition affect joints?
Joints are comprised of bones covered with a smooth cartilage layer that facilitates movement. Damage to this cartilage or other joint components like tendons or joint capsules results in osteoarthritis. Causes include injury, wear over time, and other factors.
Symptoms often include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Visible bone spurs or lumps can develop around affected joints. These signs frequently appear in hips, knees, spine, and hands. Early detection and medical consultation are essential for managing symptoms effectively.
Therapies involve physical exercises, pain relief medications, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Since each patient's condition varies, treatment plans are individualized. Understanding the differences between joint degeneration and other bone-related issues like osteoporosis is vital.
Osteoporosis, unlike osteoarthritis, involves reduced bone density, leading to porous, fragile bones prone to fractures. It impacts bones such as hips, wrists, and spine, mainly affecting the elderly. Causes include genetic factors, autoimmune diseases, or cancer. Symptoms like pain and deformities may overlap, but the conditions require different management approaches.
Medications aimed at strengthening bones, along with exercise, are common treatments for osteoporosis. Early diagnosis is key to preventing fractures and managing the disease effectively.
Both osteoarthritis and osteoporosis need attention, and timely medical intervention can improve quality of life. If you notice joint pain, stiffness, or bone fragility, consult a healthcare provider promptly.