Understanding Spondyloarthritis: Causes, Symptoms, Types, and Treatment Approaches
This article provides a comprehensive overview of spondyloarthritis, including its causes, symptoms, various types, and effective management strategies. Early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications are crucial for better quality of life. It highlights genetic, infectious, and environmental factors contributing to the condition, along with practical tips such as exercise, diet, and hydration to help control symptoms.
Sponsored

Spondyloarthritis (SpA) encompasses a group of inflammatory disorders affecting the spine and joints. Common variants include ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. The condition impacts roughly 700 out of 100,000 people, with variations in severity and specific types. Early detection and treatment are vital to managing symptoms effectively. Here’s a comprehensive overview of spondyloarthritis:
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition
Individuals carrying the HLA-B27 gene variant are significantly more prone to develop spondyloarthritis. Other genetic factors also contribute to susceptibility.
Infections
Some forms of spondyloarthritis develop after bacterial infections. For example, reactive arthritis can follow urinary tract infections or gastrointestinal infections. Research also suggests that bacterial infections may trigger ankylosing spondylitis.
Psoriasis Connection
Psoriatic arthritis is linked with psoriasis. Studies indicate that approximately 15-30% of individuals with psoriasis develop this form of arthritis.
Family History
Up to half of psoriatic arthritis patients have relatives, such as parents or siblings, with similar diagnoses.
Signs and Symptoms
Fever
Fever is common in reactive arthritis, a subtype of spondyloarthritis. Studies show around 33% of affected individuals experience elevated temperatures.
Sleep Issues
Severe pain and discomfort, especially in spinal conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, often disrupt sleep patterns.
Limited Movement
Joint and spine inflammation can cause stiffness and reduced flexibility, affecting daily activities.
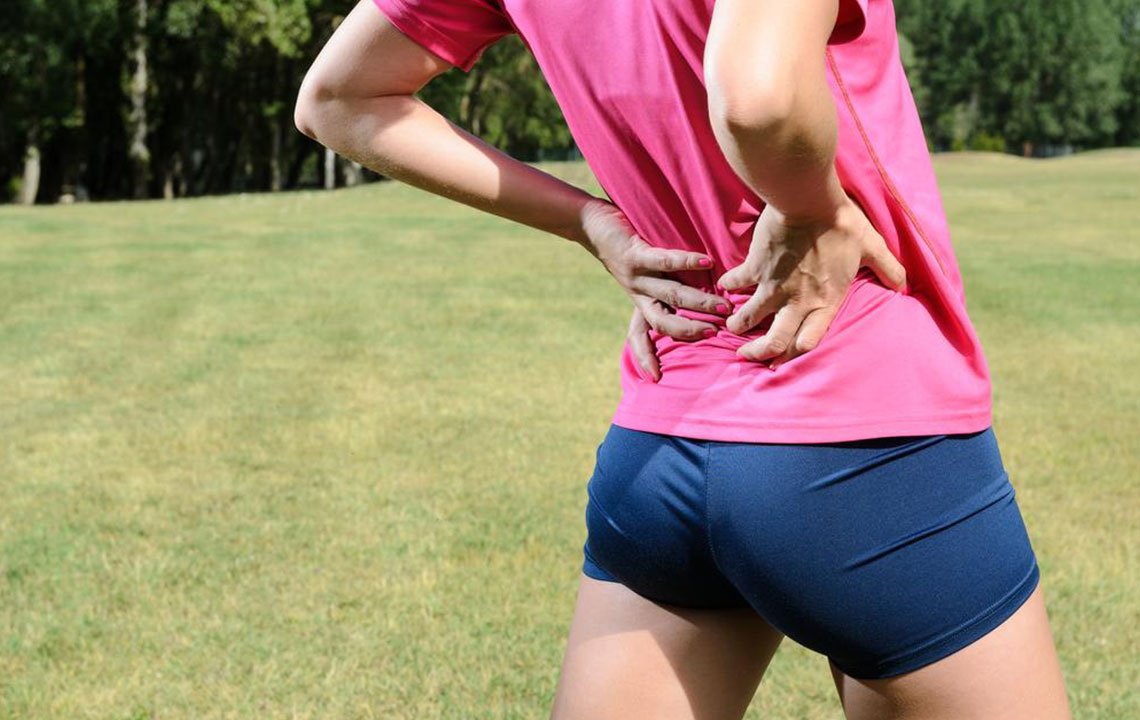
Swelling, Pain, and Tenderness
Patients may notice swelling and pain in the hips, knees, elbows, shoulders, or lower back, often worsening after prolonged inactivity.
Skin Rashes
Psoriasis-related rashes—red, scaly patches—may appear before or after joint symptoms.
Fatigue
Chronic inflammation and pain often lead to exhaustion and decreased energy levels.
Types of Spondyloarthritis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
This form involves sustained inflammation of the spine and sacroiliac joints, causing chronic back pain, stiffness, and possible breathing difficulties if ribs are affected.
Axial Spondyloarthritis
The most prevalent form, primarily affecting the spine, pelvis, and chest, often manifesting as back pain before age 45, sometimes in adolescence.
Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis
Connected with inflammatory bowel diseases, this type affects limbs and the spine, with some patients experiencing digestive symptoms.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Related to psoriasis, it features red, scaly skin patches, nail changes, and involves fewer joints than rheumatoid arthritis.
Reactive Arthritis
Develops after infections like gastrointestinal or genitourinary illnesses, characterized by urethritis, arthritis, and eye inflammation.
Management and Lifestyle Tips
Alongside medication adherence, lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms. Here are some strategies:
Exercise Therapy
Targeted exercises—stretching, strengthening, balance, and cardiovascular routines—can reduce pain and improve mobility.
Avoid Sedentary Habits
Frequent movement and stretching prevent joint stiffness and enhance flexibility.
Omega-3 Rich Diet
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), can help control inflammation and support joint health.
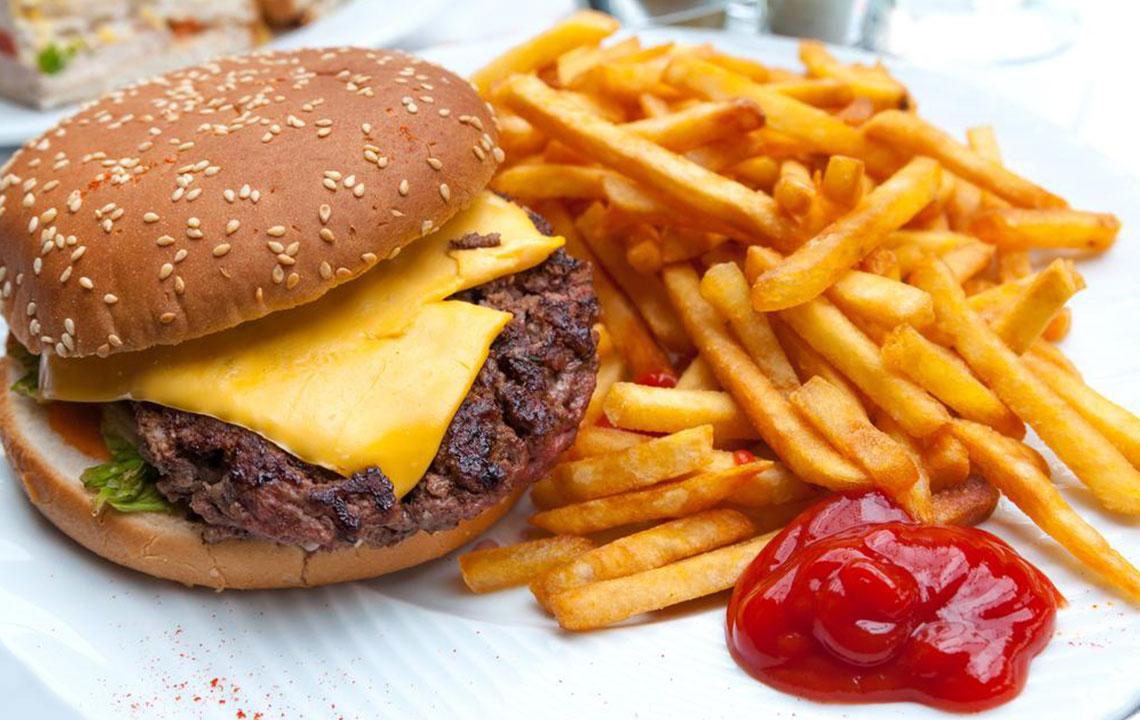
Limit Processed Foods
Processed foods with high saturated fats, sugar, and sodium may worsen inflammation and disease symptoms. Emphasize wholesome, nutrient-rich options instead.
Stay Hydrated
Water helps maintain cartilage sponginess and reduces joint stiffness. Adequate hydration is essential in symptom management.