Understanding Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Essential Facts
Learn the critical facts about diabetic ketoacidosis, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by high blood sugar and insufficient insulin. Recognize symptoms early and understand prevention and treatment options to stay healthy.
Sponsored

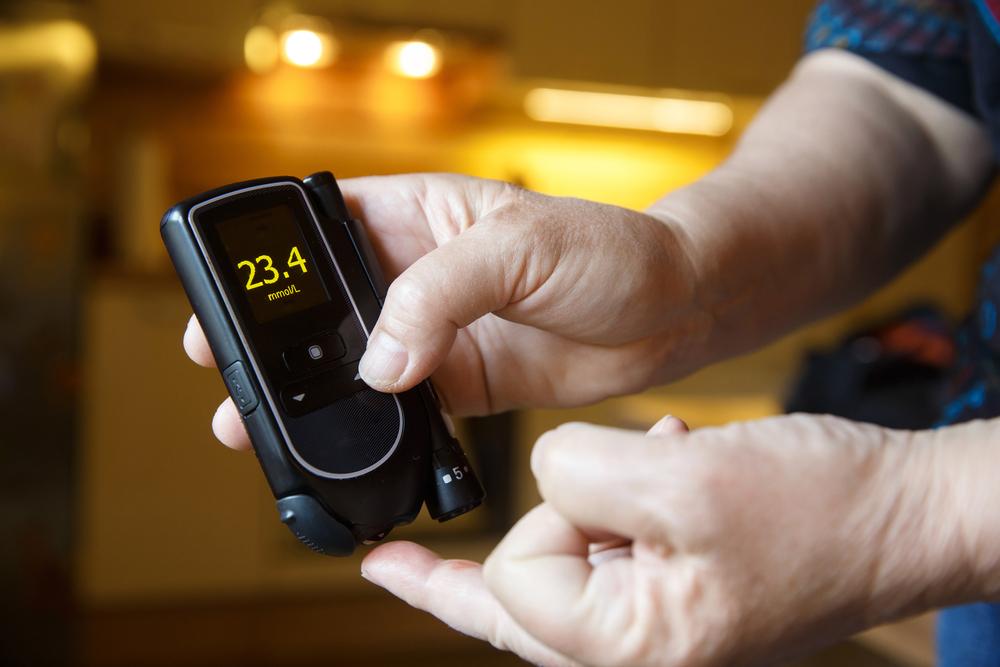
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition characterized by a dangerous increase in blood acids caused by elevated blood glucose levels. If not treated promptly, it can lead to severe health complications.
This condition occurs because insulin, which helps store excess glucose in the liver, is insufficient or absent. Without insulin, the body turns to burning fat for energy, releasing ketones into the bloodstream. Accumulation of these ketones disrupts the body's chemical balance and affects overall health.
Signs of DKA include dry mouth, excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, mild breathing difficulties, abdominal pain, fatigue, confusion, and dizziness. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment.
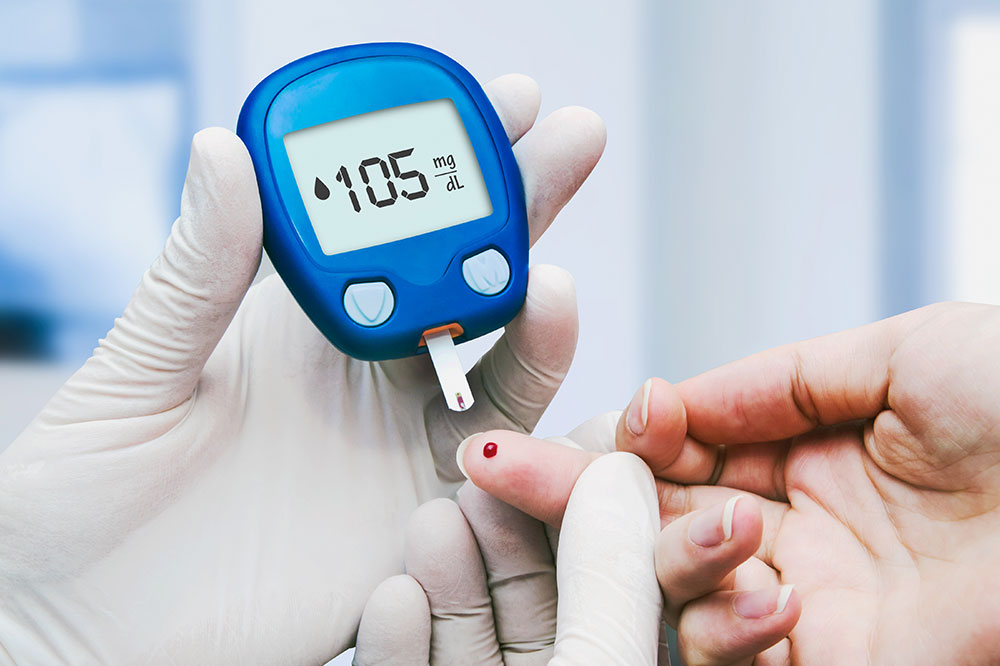
The management of DKA involves medical intervention, primarily administering insulin to reduce blood glucose and ketone levels. Staying hydrated, following a sugar-conscious diet, and regular blood sugar monitoring are vital preventive measures.
Administering insulin, often via IV, is essential to lower glucose and ketone levels.
Adopting a low-sugar lifestyle helps maintain control.
Consuming plenty of water and sugar-free beverages supports hydration and blood sugar regulation.
Following a healthy diet and exercise plan, along with prescribed medications, aids in prevention.
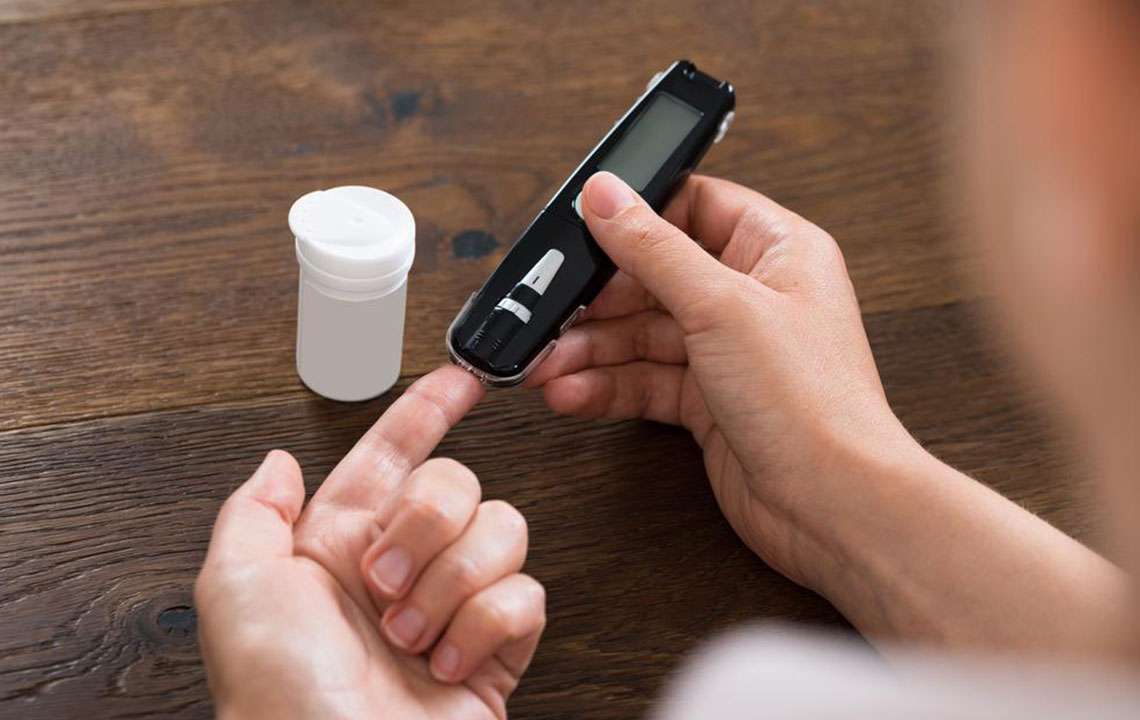
Regular blood tests help monitor glucose levels to prevent DKA episodes.